Security in the World of AI
No modern discussion of technology is complete without mention of its intersection with AI, and cybersecurity is no stranger. The market for AI in cybersecurity has blossomed, driven by greater sophistication and incidence of cyberattacks. In 2023, the AI market was valued at approximately $24.3B and is projected to expand at a CAGR of 27.8%, reaching $134B by 2030. Its growth is fueled by adoption of AI-enhanced security protocols primarily across finance, healthcare, and government.
AI is both a transformative force and a vulnerability for cybersecurity. We can approach the topic from three key perspectives:
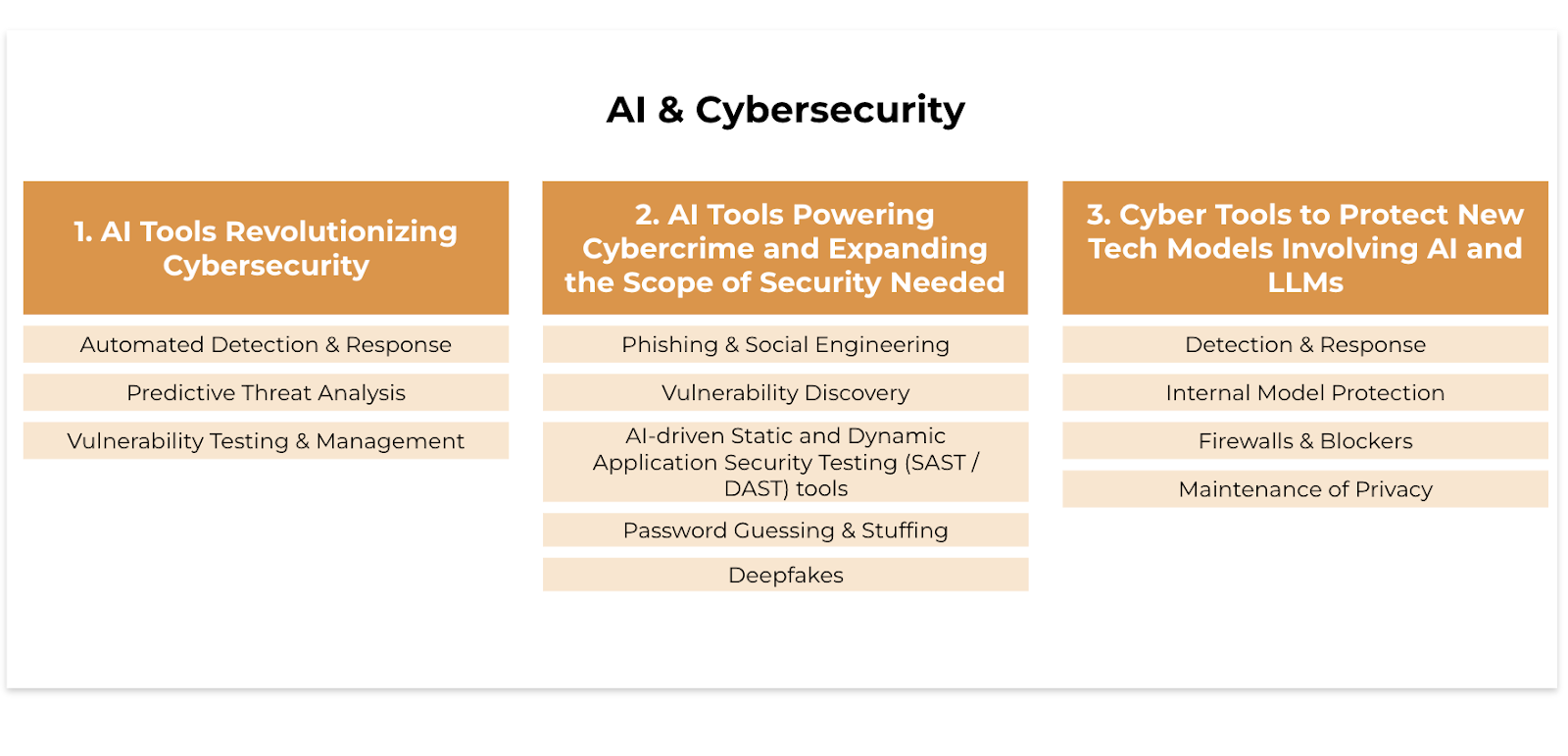
AI tools revolutionizing cybersecurity.
AI tools powering cybercrime and expanding the scope of security needed.
Cyber tools to protect new tech models involving AI and LLMs.
AI Tools Revolutionizing Cybersecurity
As cybercriminals employ more sophisticated tactics (advanced persistent threats, zero-day vulnerabilities, large-scale ransomware attacks), traditional security methods become inadequate as defense. Here, AI-powered systems can pick up the slack. AI tools offer superior capabilities in threat detection, response and prevention. Solutions can analyze vast data sets in real-time to identify anomalies and adapt to threats faster than human operators can.
Automated Detection & Response
Tools, such as those provided by the San Jose-based Securiti AI, focus on automating privacy ops to comply with global regulations, discover personal data across systems and manage consent approval and revocation. Outside its PrivacyOps platform the company also offers comprehensive model discovery to ensure compliance with global AI standards (e.g. NIST AI RMF, EU AI act) and integrates its capabilities with the customer’s data command center. Vectra AI offers automated detection & response tools to analyze networks in real time. SentinelOne does the same for endpoints.
Predictive Threat Analysis
Balbix provides automated cybersecurity posture management, enabling organizations to inventory and prioritize security risks across their IT landscape. It uses AI and machine learning to deliver predictive insights, helping to identify and mitigate potential threats before they materialize. In 2022, Balbix raised a $70M Series C led by Redline Capital. Darktrace is a self-learning AI that continuously learns and models normal behavior of systems, flagging unusual activity in cloud, network, and IoT devices.
Vulnerability Testing & Management
Axonius uses AI to automate asset discovery, vulnerability management, and compliance by integrating data from various sources into a single platform. Similarly, Snyk performs penetration testing and focuses on securing applications by leveraging AI to identify vulnerabilities in code and open-source libraries.
These solutions are invaluable, especially when considering that the average time to identify a breach can stretch into months. AI-driven cybersecurity tools enhance defense mechanisms, minimizing the financial and reputational repercussions of such incidents.
AI Tools Powering Cybercrime and Expanding the Scope of Security Needed
On the other hand, bad actors are increasingly using AI to automate hacking and bypass security measures. SlashNext’s report found a 856% increase in malicious emails in the last 12 months alone. Worse still, LLMs themselves become attack surfaces for cybercriminals. Attackers may manipulate these models, contaminate their training data, or use them to generate malicious content. The end goal is either to undermine company trust or facilitate further attacks by compromising the integrity of the models.
Most obviously, AI can be used for phishing and social engineering by creating convincing emails, voice messages, and videos that mimic human communication styles. AI can also analyze data to create detailed profiles of potential targets. Attackers are leveraging AI tools to craft highly convincing content to enable fraud schemes against individuals and businesses.
Through vulnerability discovery, AI can scan systems to find vulnerabilities that can be exploited. ML learning models are trained on datasets of normal code activity, enabling Ai to recognize deviations from the norm and flag them as hidden vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities are analyzed and used to create attack sequences to overcome a server’s defenses. Generative AI can also adapt to security systems and learn from the results of other attacks. By understanding patterns and anomalies that commonly cause security weaknesses, hackers can identify exploitable software flaws, sometimes before security teams are aware of them.
AI-driven Static Application Security Testing (SAST) tools automatically scan a program’s source code, bytecode, or binary code without executing it. AI can identify security flaws such as buffer overflows, SQL injection points, and cross-site scripting vulnerabilities by analyzing the complete codebase. By leveraging ML algorithms from previous analyses, these tools improve their ability to detect complex vulnerabilities over time. Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) tools analyze running applications to find vulnerabilities by interacting with the application, performing functions, and analyzing responses such as runtime exceptions and configurations that can be exploited.
AI-powered tools are also being used for password guessing and stuffing. For example, Hashcat is a fast, efficient, and versatile hacking tool that assists brute-force attacks by conducting them with hash values of passwords that the tool is guessing and applying. Breaches of complex passwords are on the rise as hackers use Hashcat to crack passwords using known hashes. This is next-level hacking that goes beyond the simple stuffing of credentials into username/password fields on web applications.
Deepfakes, a blend of machine learning and media manipulation, allow cybercriminals to create convincingly realistic synthetic media. Criminals then use these fakes to spread misinformation, execute financial fraud, and tarnish reputations. In the same vein, AI has been used to create fake verification documents, such as digital clones and fake IDs. These malicious tools enable fraudsters to bypass KYC procedures, set up bank accounts and exploit financial firms.
The nexus of AI and cybersecurity
Cyber Tools to Protect New Tech Models Involving AI and LLMs
The Large Language Models (LLMs) that power Generative AI companies utilize as inputs the universe of information available on the internet. This raises the concern that unsavory or falsified human content will leak in and become perpetrated by the models. Generative models are prone to supplying misinformation. Reliability – in terms of safety, relevance, correctness – is a problem.
For example, last November, OpenAI experienced a DoS attack that disrupted their API and ChatGPT services, leading to several outages. Leading AI organizations, including Anthropic and OpenAI, have stressed the importance of protecting their model weights from theft. Such thefts typically occur via compromised credentials or attacks on the supply chain.
Detection & Response
Startups have risen to combat this with tools built for self-evaluation. HiddenLayer, winner of the 2023 RSA Conference Innovation Sandbox, is effectively an extended detection & response (XDR) for AI, protecting AI models against adversarial attacks, vulnerabilities and malicious code injections. Similarly, Lasso Security focuses on securing AI and machine learning models from adversarial attacks through an XDR solution are designed to identify and prevent security breaches in AI systems. Another leader, AIShield (Powered by Bosch), offers AI-based security solutions that protect AI models during their consumption, reducing the risk of data breaches or malicious activity during operation.
Internal Model Protection
TruEra offers AI quality management tools with a focus on model explainability and performance monitoring. Witness AI intercepts activity between employees and the custom models they are using. Guardrails AI implements constraints based on common safety and reliability concerns, such as avoiding harmful content or ensuring factual accuracy, and allows organizations to define their own guardrails tailored to specific use cases and risk profiles. Fiddler AI ensures that outputs are free from biases that could cause hallucinations.
Firewalls and Blockers
Bad actors can capitalize on LLM vulnerability. The practice of contaminating training data sources to compromise model performance is called “data poisoning”. This can take place in the form of deliberately furnishing the internet with misinformation or more directly injecting data through a known attack path to contaminate the input pool.
To counter-party this movement, in a practice known as “red-teaming”, companies have popped up to provide a service simulating adversary hackers and reporting vulnerabilities. Robust Intelligence and Lakera offer – respectively – the products Algorithmic AI Red Teaming and Lakera Red. Even the White House has secured voluntary support of leading AI companies to red team their own models.
Startups like Protect AI are stepping up with tools designed to secure AI models from vulnerabilities. They offer AI firewalls, vulnerability scanning, and monitoring solutions to protect AI models from cyberattacks and ensure model integrity.
Maintenance of Privacy
Private AI focuses on protecting personally identifiable information (PII) within AI models. Their tools identify and redact PII. Nightfall specializes in data leak protection, securing sensitive information within AI models and preventing exposure. This is crucial as AI systems are increasingly tasked with handling personal and sensitive data. Tonic and Gretel also fit into this category by offering synthetic data solutions that ensure privacy while training AI models. This allows organizations to use realistic datasets without risking the security or privacy of individuals.
AI tools are helping to revolutionize cybersecurity, but they are also being used by bad actors to expand the scope of potential attacks. At the same time, new cyber tools are being developed to protect these very AI models from threats like data leaks, adversarial attacks, and malicious actors. The landscape of cybersecurity is being reshaped as AI becomes more integrated into our lives, and the rise of specialized AI security companies is a testament to the importance of this new frontier.
—————————————–
If you are a builder, investor or researcher in the space and would like to have a chat – please reach out to me at ayla.j@thelotuscapital.com