Wearable Robotics: Why Now, Who’s Leading, and What’s Next?
Wearable robotics is transforming the way we think about human augmentation. These technologies—typically in the form of exoskeletons or smart wearable devices—are designed to enhance human strength, endurance, and mobility. Originally born from research labs and military projects, wearable robots have now expanded to healthcare, manufacturing, and beyond, where they are helping people overcome physical limitations and perform demanding tasks with greater ease.
As the demand for ergonomic solutions, rehabilitation aids, and injury prevention tools continues to rise, wearable robotics is finding a home in industries ranging from healthcare to construction. Startups are at the forefront of this movement, developing lightweight, affordable devices that seamlessly integrate with the human body.
Why Wearable Robotics?
The global wearable robotics market is poised for explosive growth, driven by the convergence of advances in AI, machine learning, and biomechanics. Wearable robots, such as exoskeletons, provide assistance for physically demanding tasks or help individuals with mobility issues regain independence. As industries like manufacturing, construction, and healthcare face labor shortages and an aging workforce, the demand for wearable robotics is expected to soar.
The wearable robotics market is projected to reach $8.5 billion by 2027, fueled by the need for ergonomic solutions and injury prevention in the workplace. Roam Robotics, a California-based startup, has developed a lightweight exoskeleton designed to improve mobility for individuals with joint pain or physical impairments.
“Wearable robotics is about enhancing human potential—helping individuals move freely and perform tasks with less strain,” says Tim Swift, CEO of Roam Robotics. “We believe that wearable technology has the potential to transform both personal mobility and workforce efficiency.”
Who is Making Noise in the Industry?
Several innovative startups are making waves in the wearable robotics space, addressing needs across various sectors, including healthcare, industrial work, and defense.
Roam Robotics: Based in San Francisco, Roam Robotics has developed exoskeletons that assist with mobility and strength for individuals with knee and joint pain. Their lightweight, affordable devices are designed for both everyday users and athletes.
Ekso Bionics: This California-based startup is at the forefront of wearable exoskeleton technology for industrial and healthcare use. Their “EksoVest” is designed to reduce fatigue and injury risk for industrial workers by supporting upper body movements during repetitive tasks. “Our exoskeletons are about empowering workers to do more while staying safe,” says Jack Peurach, CEO of Ekso Bionics.
SuitX: A spin-off from UC Berkeley, SuitX focuses on affordable and practical exoskeletons for workers in industries such as construction, manufacturing, and healthcare. Their devices reduce muscle strain and fatigue for workers performing physically intensive tasks.
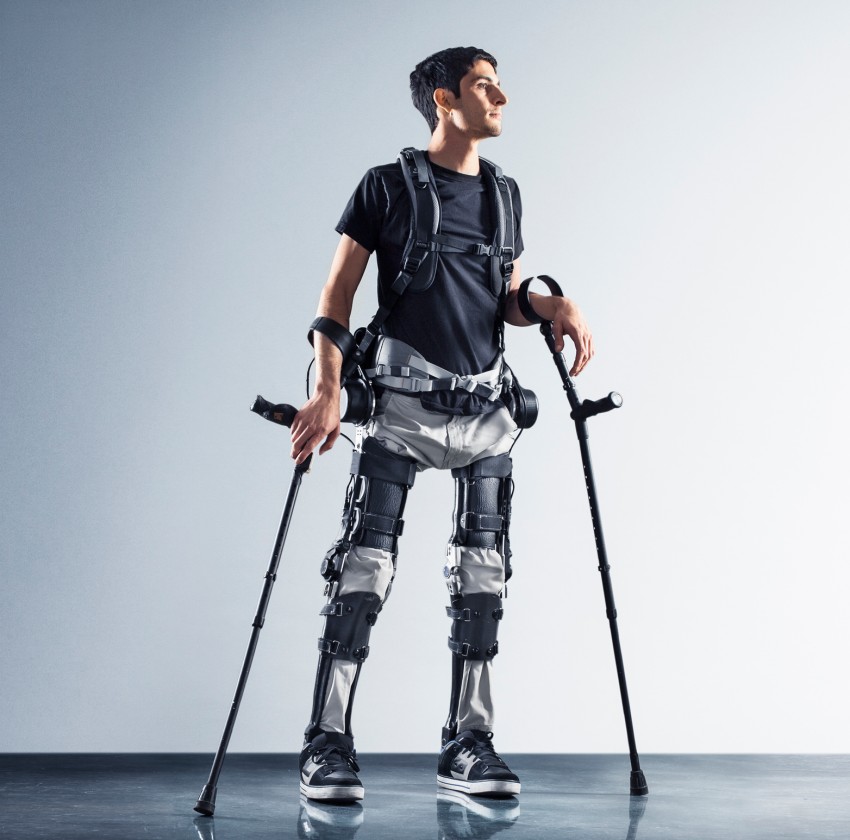

SuitX’s “Pheonix”
What is Coming Next?
The future of wearable robotics lies in creating devices that are lighter, more affordable, and more adaptable to various use cases. Startups are working to improve the AI-driven capabilities of wearable robots, enabling them to respond to real-time data and adjust movements or support levels accordingly.
Seismic, a startup that develops powered clothing, is pushing the boundaries of wearable robotics by embedding robotics into everyday clothing. Their “Powered Clothing” integrates robotics with soft textiles to assist wearers in performing physical tasks with less strain. Rich Mahoney, CEO of Seismic, notes, “We envision a future where robotic clothing will be as common as smartphones, helping people move more freely and comfortably.”
Startups like Cyberdyne, which developed the “HAL” exoskeleton for medical rehabilitation, are expanding the scope of wearable robotics to include AI-powered systems that assist patients with mobility and strength training. Their vision is to create smart exoskeletons that not only support physical movement but also learn and adapt to the user’s body over time.
In the coming years, expect to see more wearable robots integrated into everyday life, from workplace safety enhancements to rehabilitation devices that help patients regain mobility. With the rise of “Robotics-as-a-Service” (RaaS) models, wearable robots will become more accessible, allowing companies to lease these technologies without the heavy upfront costs.
—————————————–
If you are a builder, investor or researcher in the space and would like to have a chat – please reach out to me at amit.k@thelotuscapital.com